Java allows you to declare one try block within another try block. Nested try blocks are used when a part of the try block throws one exception and the complete try block throws another exception thus nested try blocks are used.
Syntax-
try
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
try
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
Example-
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
try{
System.out.println("going to divide");
int b =48/0;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println(e);}
try{
int a[]=new int[10];
a[10]=6;
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println(e);}
System.out.println("code");
}
catch(Exception e){System.out.println("handeled");}
System.out.println("normal program flow");
}
}
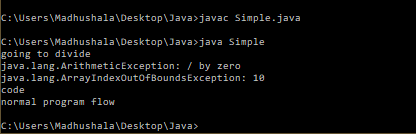
Output-